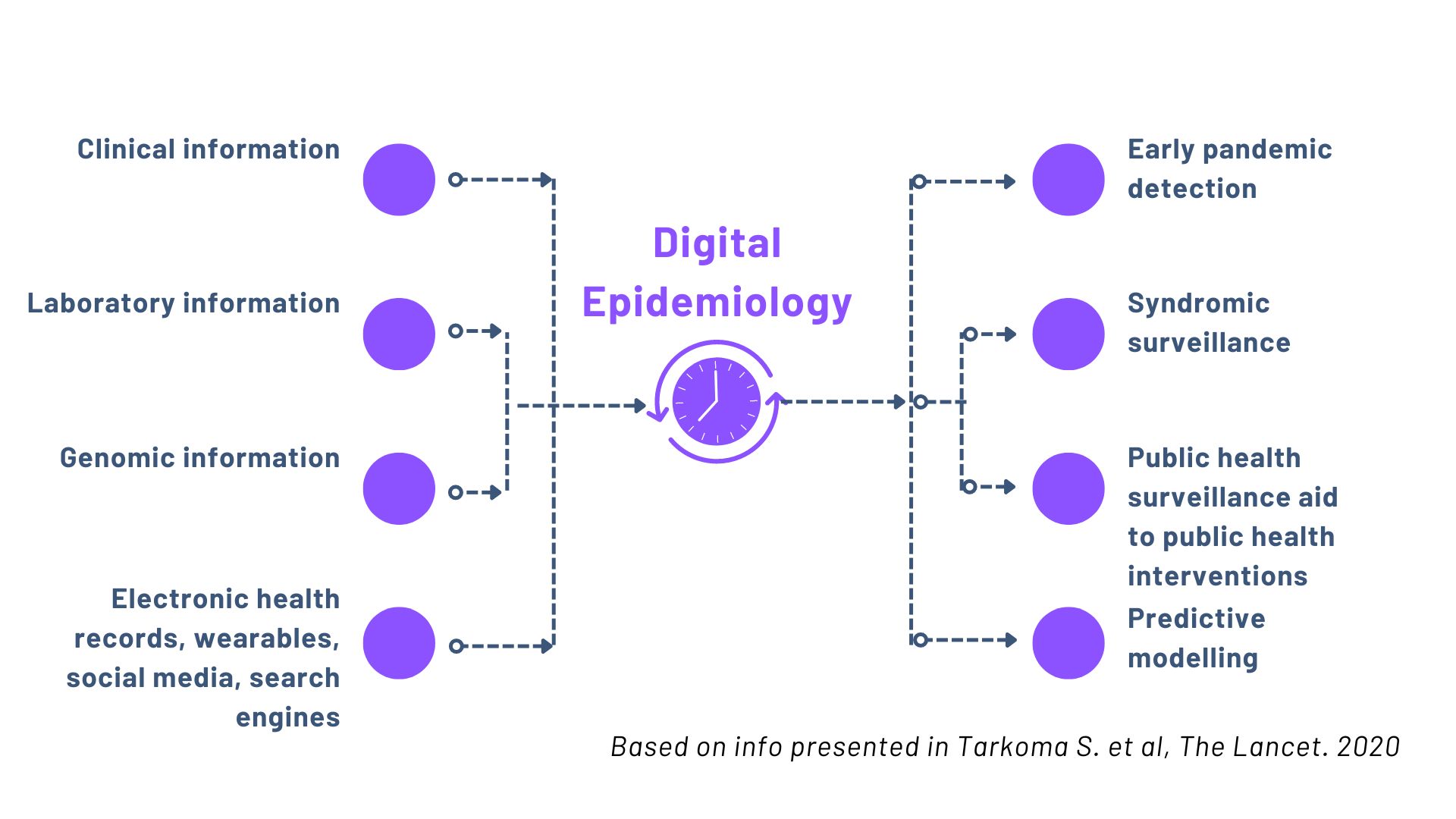
What is Digital Epidemiology?
The importance of Digital Epidemiology
“Digital epidemiology is epidemiology building on digital data and tools” (Salathé M. et al, Life Sci Soc Policy. 2018)
Funded by the NIHR under the Global Health Research Unit programme, our work at the Centre for Genomic Pathogen Surveillance focuses specifically on the applications of digital epidemiology of infectious diseases, including outbreak investigations, pathogen surveillance, understanding of vaccine efficacy and spread of antimicrobial resistance genes and vehicles.
The importance of digital epidemiology has been raised to a global level during the pandemic. The value of bringing together genomic with epidemiological and clinical data improved public health decision making, informing experts with regard to virus variants expansions and adding significant contributions to the investigation on the origin of the virus.
Moreover, the pandemic has taught us that the effective use of digital epidemiology can impact on operational decisions in healthcare settings, impacting on patient wellbeing and outcomes.
During the COVID pandemic there has been a learning curve for many laboratories around the world, who were able to use genomic and digital data to good effect, changing operational approaches and decisions based on results. However, interdisciplinary teams formed of wet-lab scientists, Bioinformaticians, clinicians and non-technical staff (hospital managers, for example) often found barriers in communication of information. The relevance and impact of Digital Epidemiology was often difficult to explain between different professional specialisations. Scientists familiar with Digital Epidemiology often found it challenging to communicate to colleagues what genomic data could and could not reveal.
There is a general need to learn how to interpret information related to Digital Epidemiology and to better communicate results to various stakeholders.